
Aerobic Respiration KS3 Lower Ability Teaching Resources
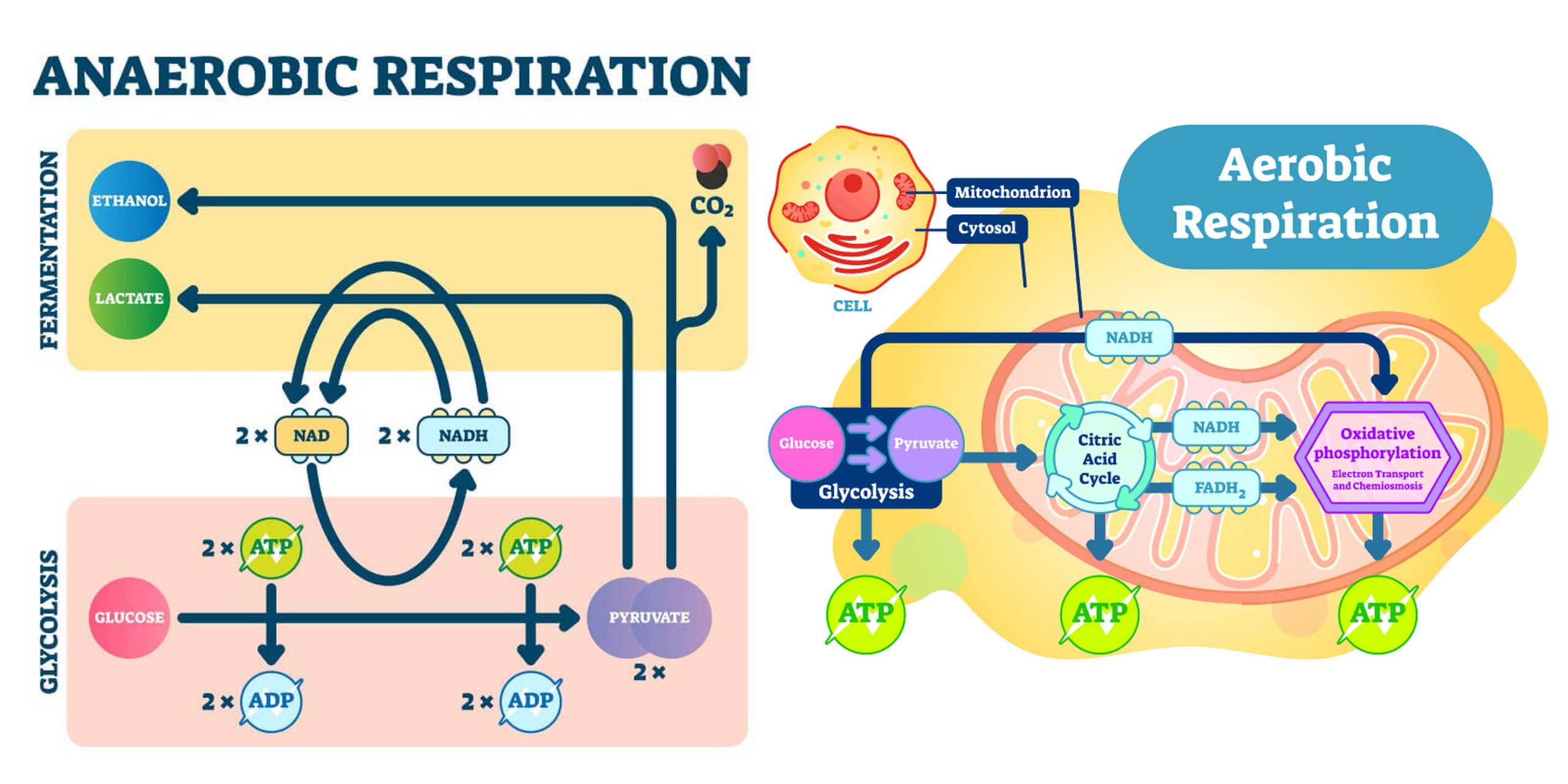
Diagram: Aerobic respiration . Definition. Anaerobic Respiration is the process of respiration that takes place in the absence of oxygen, or in the limited supply of oxygen. The final electron acceptor in this type of respiration is not oxygen, but some inorganic ion.

Differences Between Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration ProtonsTalk
A diagram shows the step-down flow of electrons to create ATP. Electrons are represented by a picture of a sun with an e and negative symbol in the center.. Cellular respiration is an absolutely essential process for any cell because it's how it produces energy. Cells need energy for all kinds of things: moving things around, producing.
√ Aerobic Respiration / Respiration Respiration Is The Release Of
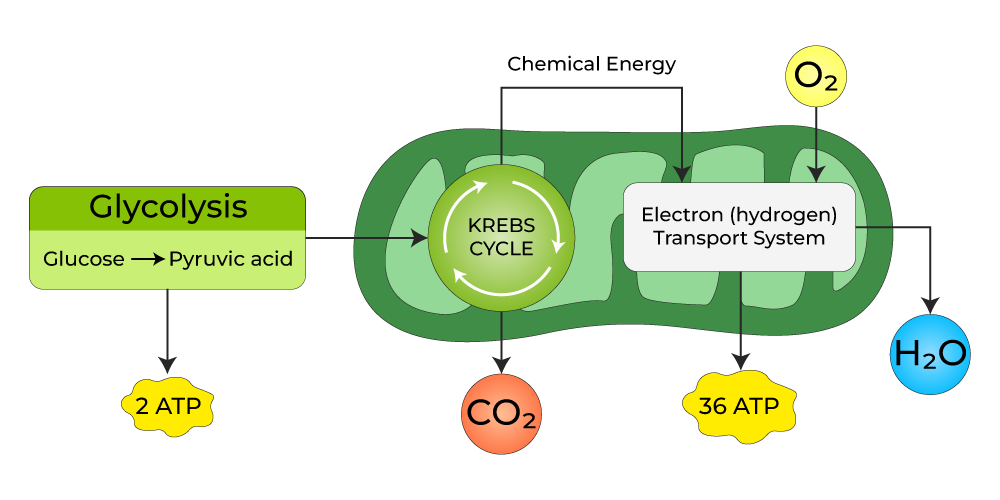
The following cellular respiration diagram illustrates the major steps of aerobic cellular respiration. In brief, food energy from fats or starches is converted into molecules of glucose.
Difference between Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration Aerobic vs
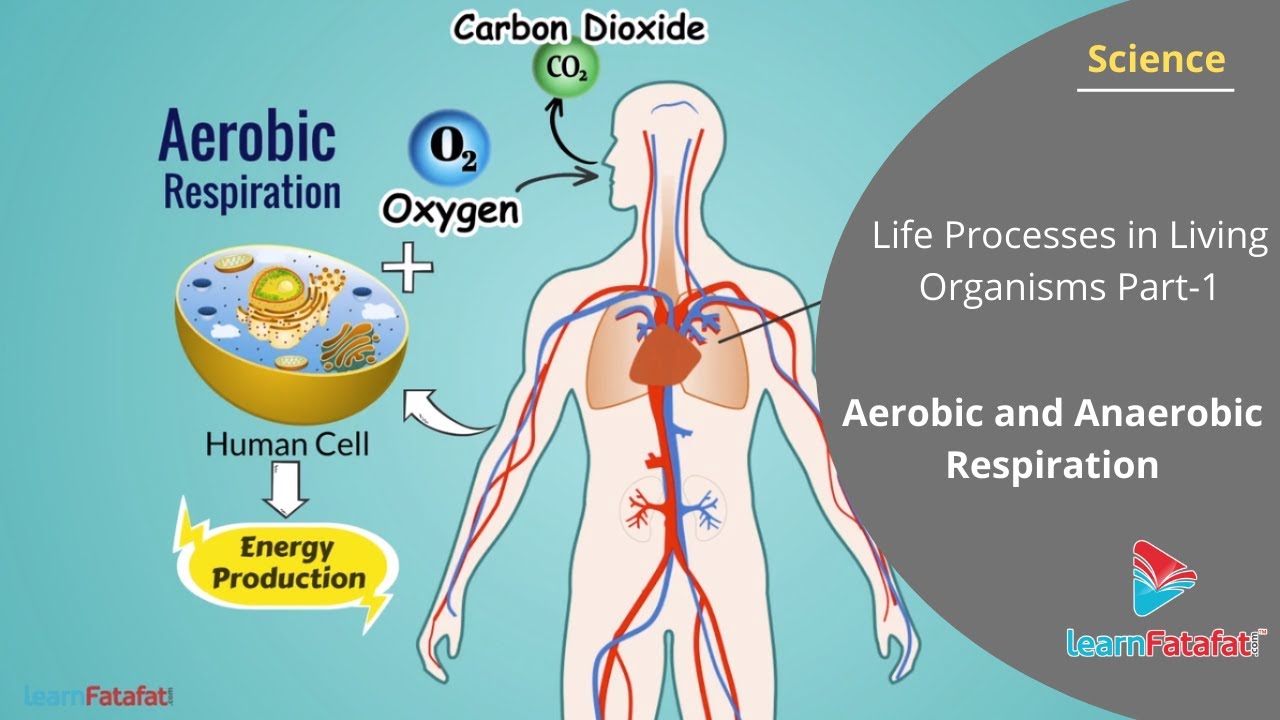
Aerobic close aerobic With oxygen. respiration needs oxygen. It is the release of a relatively large amount of energy in cells by the breakdown of food substances in the presence of oxygen . It.

Aerobic Respiration 88Guru
A cellular respiration diagram showing the overall three step process of aerobic cellular respiration, from glucose in glycolysis to the electron transport chain. In this diagram, the citric acid.
Detailed Cellular Respiration Diagram
Cellular respiration can occur both aerobically (using oxygen), or anaerobically (without oxygen). During aerobic cellular respiration, glucose reacts with oxygen, forming ATP that can be used by the cell. Carbon dioxide and water are created as byproducts. The overall equation for aerobic cellular respiration is:
Aerobic Respiration Carlson Stock Art
Aerobic Respiration: Definition, Steps and Process. Organisms such as prokaryotes and eukaryotes use respiration mechanisms for the breakdown of food that may require environmental oxygen. The process by which mitochondria use to transfer the energy in foods to ATP is known as cellular respiration. In this process, a food molecule breaks down.
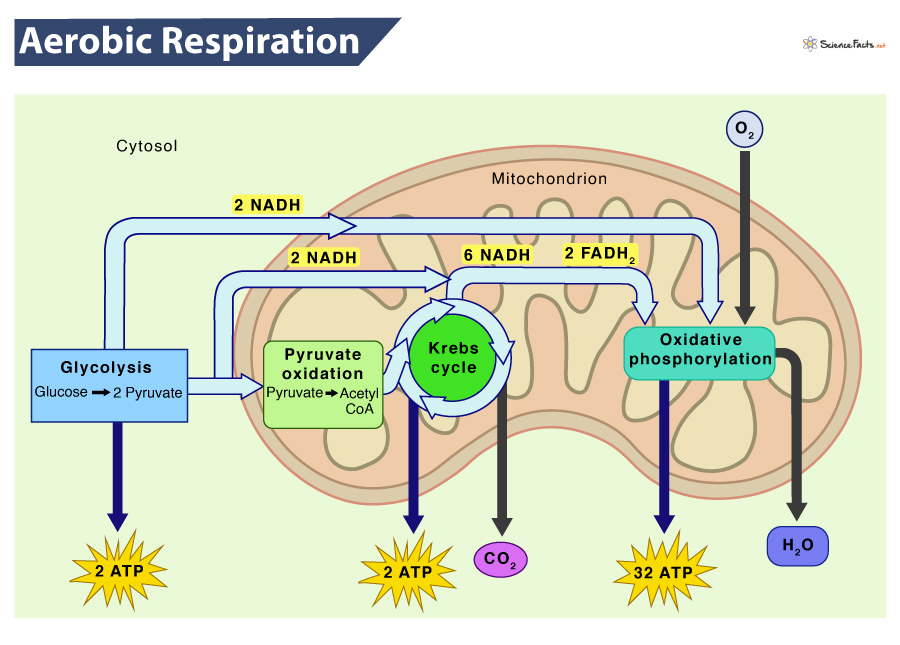
Aerobic Respiration
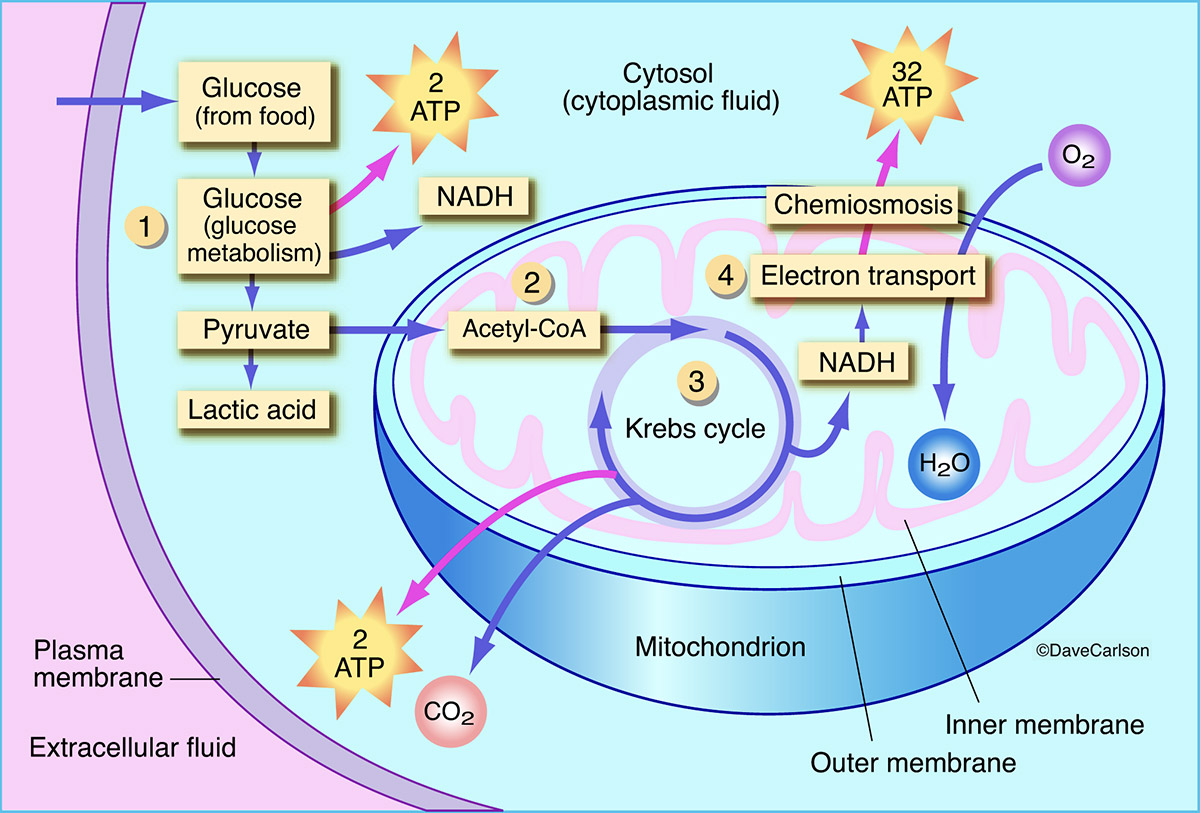
Figure 5.9.3 5.9. 3: Cellular respiration takes place in the stages shown here. The process begins with Glycolysis. In this first step, a molecule of glucose, which has six carbon atoms, is split into two three-carbon molecules. The three-carbon molecule is called pyruvate.

Glycolysis Steps Biology Dictionary
8.1.3 Draw and label a diagram showing the structure of a mitochondrion as seen in electron micrographs. Figure 8.1.2 - Labelled diagram of a mitochondrion. 8.1.4 Explain aerobic respiration, including the link reaction, the Krebs cycle, the role of NADH + H +, the electron transport chain and the role of oxygen. Aerobic Respiration

√ Aerobic Respiration / Respiration Respiration Is The Release Of
Step 1: Glycolysis. When glucose is transported into the cytoplasm of cells, it is broken down into two molecules of pyruvate (Figure 4.1.2.2 4.1.2. 2 ). This process is called glycolysis (glyco- for glucose and -lysis, meaning to break apart). Glycolysis involves the coordinated action of many different enzymes.

Aerobic Respiration CELLULAR RESPIRATION
The process of aerobic respiration using glucose can be split into four stages. Each stage occurs at a particular location in a eukaryotic cell: Glycolysis takes place in the cell cytoplasm. The Link reaction takes place in the matrix of the mitochondria. The Krebs cycle takes place in the matrix of the mitochondria.

Aerobic Respiration Bio Anatomical Vector Illustration Diagram Labeled
Steps of cellular respiration. During cellular respiration, a glucose molecule is gradually broken down into carbon dioxide and water. Along the way, some ATP is produced directly in the reactions that transform glucose. Much more ATP, however, is produced later in a process called oxidative phosphorylation. Oxidative phosphorylation is powered.
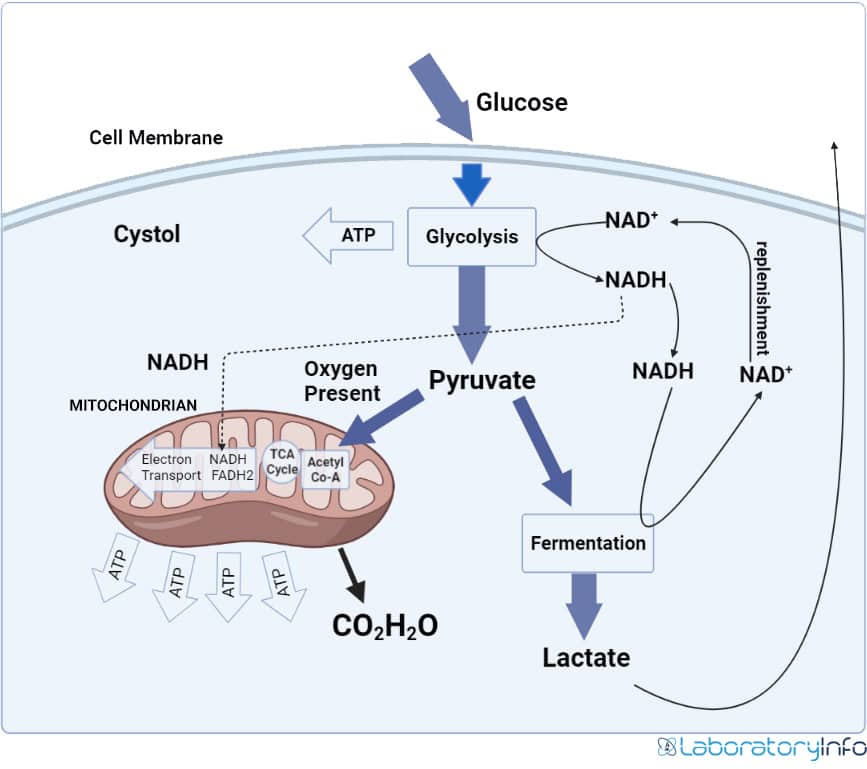
Aerobic Respiration and Anaerobic Respiration Diagrams, Definition
Aerobic respiration is the process by which glucose molecules are broken down into usable cellular energy called adenosine triphosphate (ATP) while in the presence of oxygen. This cellular process.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/aerobic_cellular_respiration-5c37aa17c9e77c0001c3f665.jpg)
Respiration Definition and Types
Aerobic respiration is the cellular respiration process that occurs in the presence of oxygen. It is the respiratory process where the electron is transferred to dioxygen molecules (O 2 ), generating water molecules and energy molecule ATP. Here glucose molecule is completely oxidized into energy (ATP), carbon dioxide, and water.

biochemistry How does the body switch between aerobic and anaerobic
Aerobic respiration is the process by which organisms use oxygen to turn fuel, such as fats and sugars, into chemical energy. In contrast, anaerobic respiration does not use oxygen. Respiration is used by all cells to turn fuel into energy that can be used to power cellular processes. The product of respiration is a molecule called adenosine.
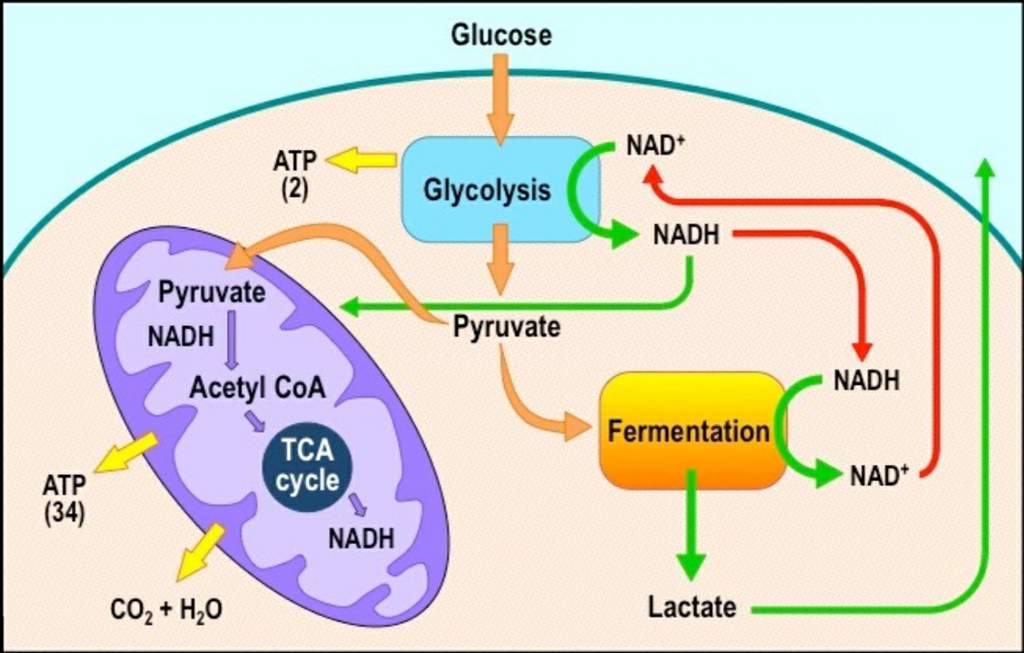
Aerobic and anaerobic cellular respiration Science Amino
Aerobic respiration produces energy, much more efficiently than anaerobic respiration, but is a slower process. Anaerobic respiration does not require oxygen. Lactic acid is produced as a by-product.